More than a third of U.S. adults are Obese.
Obese is a medical term that means you weigh at least 20% more than what is ideal for your height, often because of body fat. It’s measured by BMI (body mass index): 30% and higher is considered obese. That extra weight, especially as fat around your waist, can lead to health issues that often feed off of each other. Shedding pounds may prevent, slow, or even reverse many of them.Symptoms associated with Obesity:
 Your larger body may prevent your lungs from expanding fully, and your breathing muscles may not work as well, so you can’t take enough air in.
Your larger body may prevent your lungs from expanding fully, and your breathing muscles may not work as well, so you can’t take enough air in.
Inflammation linked to belly fat may also affect your lungs. You could get winded quickly while doing simple activities like climbing stairs. Extra weight can make asthma symptoms and COPD worse.
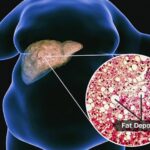 When fat builds up in your liver, it may make scar tissue (a condition known as cirrhosis) that can eventually shut your liver down completely. Symptoms may not appear until the damage is done.
When fat builds up in your liver, it may make scar tissue (a condition known as cirrhosis) that can eventually shut your liver down completely. Symptoms may not appear until the damage is done.
Doctors don’t know exactly what causes fatty liver disease, but you’re more likely to have problems when you’re overweight, especially in middle age.
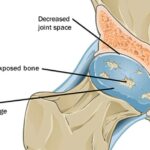 More weight puts more strain on your joints and on the cartilage that protects the ends of your bones, causing pain and stiffness. More body fat may also trigger more inflammation. Just 5% less body weight will take pressure off of your hips, lower back, and knees.
More weight puts more strain on your joints and on the cartilage that protects the ends of your bones, causing pain and stiffness. More body fat may also trigger more inflammation. Just 5% less body weight will take pressure off of your hips, lower back, and knees.
(That’s dropping from 200 pounds to 190.) Exercise is one of the best things you can do for arthritis. Talk to your doctor about what kind and how much is right for you.
 While your genes have some influence, what you eat and how much you exercise also play a role. Unhealthy foods can raise your weight and your “bad” LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
While your genes have some influence, what you eat and how much you exercise also play a role. Unhealthy foods can raise your weight and your “bad” LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
Foods with soluble fiber — like oats and other whole grains, beans, apples, grapes, strawberries, eggplant, and okra — will help get your cholesterol down as well as fill you up so you eat fewer calories.
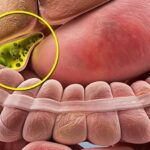 If bile, a type of digestive fluid, doesn’t move through your gallbladder like it should, it could harden into pebbles. The most common type is made up of mostly cholesterol.
If bile, a type of digestive fluid, doesn’t move through your gallbladder like it should, it could harden into pebbles. The most common type is made up of mostly cholesterol.
Obese women have higher odds of getting them. You may have more cholesterol in your bile because your blood cholesterol or triglyceride levels are high (or you take medicine to lower them) or you have extra estrogen from birth control, hormone replacement therapy, or pregnancy.
 Belly fat is linked to insulin resistance. That’s when your body makes insulin, but your cells can’t use it properly to get glucose out of your blood.
Belly fat is linked to insulin resistance. That’s when your body makes insulin, but your cells can’t use it properly to get glucose out of your blood.
Higher-than-normal blood sugar can become diabetes and may lead to trouble with your heart, nerves, eyes, and more. About 8 out of 10 people who get type 2 diabetes are overweight. There’s no cure once you have it, but losing weight may help with its symptoms and prevent complications.
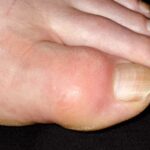 Built-up uric acid in your body can form needle-like crystals that make joints like your big toe, ankle, or knee hurt.
Built-up uric acid in your body can form needle-like crystals that make joints like your big toe, ankle, or knee hurt.
The likelihood of a flare goes up with the number on the scale and the amount of belly fat, especially when you have high blood sugar and cholesterol problems, too. A heart-healthy diet and exercise habits may help lower the level of uric acid as well as your weight.
 When your body is large, your heart has to pump harder to get blood to all of your cells. That force pushes on your artery walls and may be damaging them.
When your body is large, your heart has to pump harder to get blood to all of your cells. That force pushes on your artery walls and may be damaging them.
Your doctor will probably recommend that you exercise 20-30 minutes most days, limit sodium to 1,500 milligrams a day, and don’t smoke. Getting your BMI close to 25 often helps bring blood pressure down.
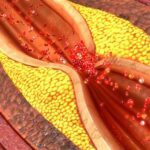 Obesity — and diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and inflammation related to it — can wear on your arteries, turning them thick and stiff.
Obesity — and diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and inflammation related to it — can wear on your arteries, turning them thick and stiff.
Narrow or clogged vessels can’t get enough blood to the cells in your organs and tissues. Although you may not have any symptoms at first, this poor circulation may eventually lead to a heart attack, heart failure, or a stroke.
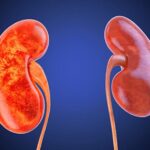 Your kidneys filter blood and help control your blood pressure. But they can’t do their jobs when fat builds up inside them and presses on blood vessels, or when the vessels that bring blood to them are clogged.
Your kidneys filter blood and help control your blood pressure. But they can’t do their jobs when fat builds up inside them and presses on blood vessels, or when the vessels that bring blood to them are clogged.
That can lead to a dangerous buildup of waste in your body. Kidney disease can be a complication of diabetes and high blood pressure, yet it can also be partly a direct result of obesity.
 A chubby neck can narrow your airway, making it harder to breathe at night. You might snore loudly or stop breathing for several seconds over and over.
A chubby neck can narrow your airway, making it harder to breathe at night. You might snore loudly or stop breathing for several seconds over and over.
When that happens, you aren’t getting the restful sleep you need. It can make you tired and groggy and lead to mood, memory, and heart problems.
 Moms-to-be who are overweight are more likely to get gestational diabetes and preeclampsia, dangerously high blood pressure that can harm both you and your baby.
Moms-to-be who are overweight are more likely to get gestational diabetes and preeclampsia, dangerously high blood pressure that can harm both you and your baby.
There’s a greater chance that you’ll need a C-section to give birth and that your baby could be born too soon, be stillborn, or have brain or spinal cord problems. Work with your doctor to manage your weight safely when you’re pregnant.
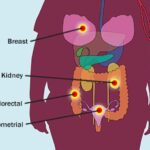 When you gain weight as an adult, whether or not it makes you obese, you’re more likely to get some cancers, including breast, colorectal, endometrial, and kidney.
When you gain weight as an adult, whether or not it makes you obese, you’re more likely to get some cancers, including breast, colorectal, endometrial, and kidney.
It might be because fat cells make hormones that change how cells grow. Or it might be that habits that lead to weight gain are similar to those that lead to cancer. Eat healthily and stay active to help avoid cancer, regardless of your weight.
![]()


























